By sharing knowledge, experience and views in the field of forging technology, we help you understand, learn and apply relevant technologies.

Hulk Metal Forging Technology
Share technical experience
-
Home>
-
Blog>
-
Technology>
What is steel forging?
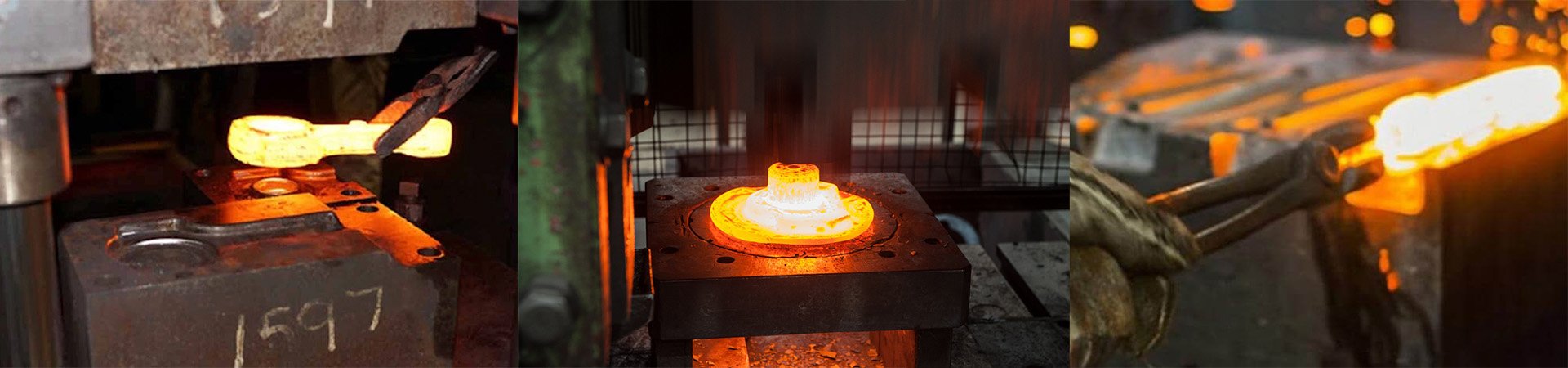

Steel forging is a process method that uses forging technology to manufacture steel forgings and forgings. It is also a key manufacturing step in the steel production process. Through forging, steel can be plastically deformed into a specified shape and size, thereby improving the internal organizational properties and mechanical properties of the material. Steel forging is widely used in various fields such as machinery manufacturing, the automobile industry, construction engineering, and mining, and is an indispensable and important process for modern industrial production.
Comparison between steel forging and steel casting
Process differences
There are significant differences in the manufacturing process between forged steel and cast steel:
Forging is to apply pressure to the metal to cause it to undergo plastic deformation under solid conditions, thereby changing its shape and properties.

Casting is to heat the metal to a liquid state and pour it into a mold, and then cool and solidify it to form a part.

Performance differences
Steel forging parts usually have the following performance advantages:
Higher mechanical properties
steel forging parts are significantly superior to cast steel parts in strength, toughness and impact resistance, and are suitable for high-stress and high-impact working conditions.
Uniform organization
The forging process can eliminate casting defects (such as porosity and looseness) and optimize the fiber structure of the metal, thereby significantly improving the internal density of the material.
Adapt to complex loads
Steel forging parts can withstand complex dynamic loads and are suitable for manufacturing key mechanical parts such as shafts, gears, and connecting rods.
Steel casting, due to its process characteristics, is more suitable for manufacturing parts with complex shapes that cannot be formed by forging or cutting. For example, cast carbon steel is suitable for high-strength structural parts, cast low-alloy steel meets corrosion resistance requirements, and cast special steel can cope with extreme working environments.
Analysis of the advantages of steel forging
Strength and durability
Steel forging parts perform well in high-load, strong vibration, and high-impact environments due to their high strength-to-weight ratio. Its excellent durability makes it the preferred material for manufacturing key load-bearing parts.
Precision and design freedom
Forging technology can achieve tighter tolerances and higher dimensional accuracy to meet high-precision assembly requirements. In addition, forgings usually have a smoother and more uniform surface quality in appearance, which helps to improve the aesthetics of the finished product. At the same time, the forging process allows the design of more complex shapes and structures, thereby expanding the functions and application range of the product.
Economy and efficiency
The advantages of forging parts in service life and strength make them more economical in long-term use. Especially under high-intensity working conditions, forging parts can effectively reduce the frequency of equipment maintenance and replacement, thereby reducing overall costs.
Steel forging manufacturing process
Forging processes can be divided into the following three categories according to the forming temperature:
Hot forging
Hot forging is the process of heating steel to above the recrystallization temperature for forging. This process greatly reduces the deformation resistance of the material and improves the plasticity of the material. Hot forging is suitable for the manufacture of large forgings and high-plasticity parts.
Warm forging
Warm forging is a forging process performed between the recrystallization temperature of steel and room temperature. Compared with hot forging, the warm forging process can obtain higher surface accuracy and smaller deformation resistance and is the preferred process for the processing of small and medium-sized complex parts.
Cold forging
Cold forging is the direct forging of steel at room temperature. Cold-forged parts have excellent dimensional accuracy and surface quality, but due to their large deformation resistance, they are generally suitable for the production of small parts or thin-walled parts.
Analysis of steel forging types
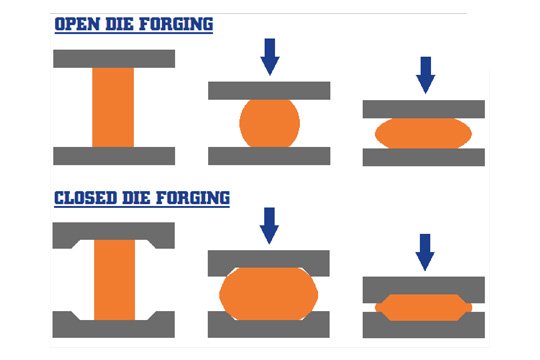
Free forging
Free forging uses an open die to gradually shape the metal through multiple hammering or pressing. This process is suitable for processing forgings with simpler shapes and larger sizes.
Closed die forging
Closed die forging uses precision dies to completely cover and press the metal into shape, which can achieve the production of forgings with complex shapes and higher precision. This process has significant advantages in manufacturing mass-produced, high-precision parts. Get more details about the process differences in our article Forging: What Is It? What Are The Different Types of Hot Forging?
Wide application of forged steel
Agricultural and forestry equipment
Agricultural and forestry equipment needs to withstand heavy loads and impacts in complex environments. Forgings (such as plowshares, tillage tools, and logging equipment) are ideal manufacturing choices due to their excellent strength and toughness.
Engineering and mining machinery
The application of forged parts in engineering and mining machinery covers key equipment such as bulldozers, cranes, and excavators. Forged steel parts can withstand high-intensity working pressure and strain, ensuring the reliability and long life of equipment in harsh environments.
Power Tools
Steel forgings are widely used in the power industry. We can manufacture jaw wire grips for copper cable, covered cable, guy wire, wire rope, aerial bundled cable (conductor), bare aluminum, ACSR, ACSS, AAC, and so on. All products are made of high-quality steel and processed by advanced hot die forging technology, with excellent mechanical properties and durability.
Fasteners and Industrial Hardware
Forged steel fasteners and hardware (such as bolts, nuts, etc.) are widely used in industry. Their excellent wear resistance and corrosion resistance make them an important part of the construction and machinery fields.
Automobile and Transportation
Forged steel parts are widely used in the automotive and transportation industries. For example, axles, suspension systems, and engine components all rely on the strength and durability of forged steel parts to ensure the safe operation of vehicles under various working conditions.
Steel forging plays an important role in modern industrial production with its strong performance advantages and flexible design capabilities. From the automotive industry to mining machinery, from fasteners to new energy fields, the demand for forged steel parts continues to grow. With excellent process technology and strict quality control, the steel forging industry will continue to promote the innovative development of material science and manufacturing technology.
Article Navigation
Article Navigation
Industries
Foundries
-

July.01, 2024
Difference between hot forging and cold forging
READ MORE
-

June.27, 2024
What are the advantages and disadvantages of the hot forging process?
READ MORE
-

January.18, 2024
Forging: What Is It? What Are The Different Types of Hot Forging?
READ MORE
-

November.08, 2024
How to produce high-quality wire pulling grips?
READ MORE
-

July.30, 2024
What are the materials for hot forging?
READ MORE
-

July.03, 2024
What are the processes of hot forging?
READ MORE








